- Arthrodesis
- Anterior Cruciate Ligament Surgery
- Post traumatic deformity correction
- Congenital deformity correction
- Osteotomy
- Ortho-oncology
- Carpal Tunnel Release
- Arthritis
- Swellings like Ganglions,giant cell tumors of tendon sheath
- Tendon repairs, grafts and transfers
- Toe-transfers
- Complex Fractures; Non-union, Infectious
- Synovectomy
( This is a partial list. Please Enquire for the procedure you need and we will respond! )
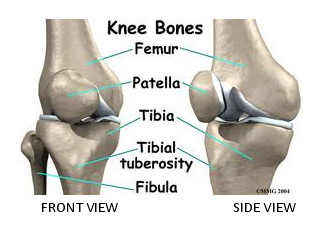
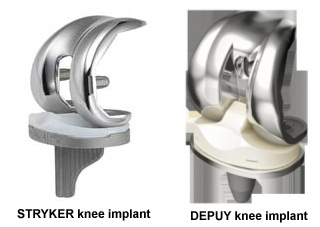
Knee Replacement Surgery (Knee Arthroplasty):
Knee replacement surgery, also known as Total Knee Replacement or Knee Arthroplasty, is performed by expert surgeons using world class implants with a success rate of 99 % in India. This procedure, involves removal of damaged joint surfaces within the knee and their replacement with artificial prosthesis made of metal, plastic or ceramic.
Total knee replacement becomes necessary when the cartilage within the knee becomes extensively worn out, primarily because of inflammation caused by osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, gouty arthritis, and lupus arthritis.
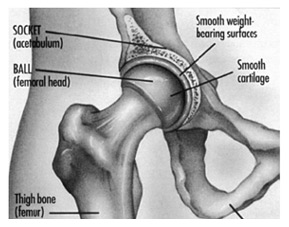
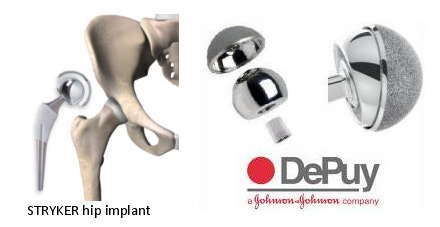
Hip Replacement Surgery ( Hip Arthroplasty):
Hip Resurfacing Surgery is bone conserving surgery that seeks to achieve functional results similar to that of a hip replacement procedure, but in doing so adopts a more conservative surgical approach which minimises bone mass removal from the hip joint, and also uses a smaller implant.
During standard hip replacement surgery, the surgeon would remove the entire ball of the ' ball and socket joint' of the hip. In the case of hip resurfacing surgery, the ball would be left intact and a metal cap is placed around the cartilage section that has worn away. The top of the femoral head is re-shaped so that its profile is closely matched to the underside of the cap of the implant. This metallic cap protects the cartilage from further deterioration. This approach leaves a large amount of bone which supports the metal cap. The other component of the implant is a metal cup that becomes the socket of the joint. The implant used in hip resurfacing surgery is much smaller than the implant used in hip replacement surgery.
Hip Resurfacing Surgery:
Hip Resurfacing Surgery is bone conserving surgery that seeks to achieve functional results similar to that of a hip replacement procedure, but in doing so adopts a more conservative surgical approach which minimises bone mass removal from the hip joint, and also uses a smaller implant.
During standard hip replacement surgery, the surgeon would remove the entire ball of the ' ball and socket joint' of the hip. In the case of hip resurfacing surgery, the ball would be left intact and a metal cap is placed around the cartilage section that has worn away. The top of the femoral head is re-shaped so that its profile is closely matched to the underside of the cap of the implant. This metallic cap protects the cartilage from further deterioration. This approach leaves a large amount of bone which supports the metal cap. The other component of the implant is a metal cup that becomes the socket of the joint. The implant used in hip resurfacing surgery is much smaller than the implant used in hip replacement surgery.
Shoulder Replacement Surgery:
Shoulder replacement surgery is a procedure for replacing the shoulder joint in order to treat acute arthritis or traumatic shoulder injury. The ends of the damaged upper arm bone and the shoulder bone (scapula) are replaced or capped with artificial materials of plastic or metal. Depending on the implant used, the shoulder joint is kept in place either by a special cement or by facilitating the organic growth of bone which happen over a period of time.
Ankle Replacement Surgery:
Ankle replacement surgery is performed to replace the damaged articular surfaces of the three bones of the ankle joint with artificial implants. This procedure is now being preferred to arthrodesis (fusion of the bones) because ankle replacement surgery restores range of motion to the joint. The surgery is normally offered to patients with arthritis who do not suffer from osteoporosis of the ankle.
Partial Knee Replacement ( Unicompartmental Knee Replacement):
Partial knee replacement is minimally invasive surgery in which only the most affected cartilage tissue of the knee joint is removed. Artificial implants of metal or plastic are placed on top of the shin bone and .below the thigh bone. If necessary, a and a patellofemoral replacement is placed below the kneecap The partial knee surgery can be done only if the arthritis in the knee is not widespread, if the ligaments are strong and if the patient is not obese.
Ilizarov Procedure / Bone lengthening
The Ilizarov Procedure is practised very successfully in India. This technique, pioneered by Dr Ilizarov of Russia in the mid-1950s, involves the creation of an artificial gap between bone ends by stretching the bones apart minutely, day after day, during the treatment period using an external device. The gap that is thus created is filled in naturally by the body by the generation of new tissue-bone, nerves, blood vessels, etc. Over a period of time, the limb can be lengthened by up to 6 inches. The technique when practised by an expert specialist, results in steady lengthening of the limb and good generation of strong bone tissue.
The meniscus cartilage is the key components of the anatomy of the knee. Meniscus tears along the outer rim can be repaired using minimally invasive arthroscopic surgery with excellent results. If the meniscus repair is in the central section, the blood supply to this area is not good enough to enable successful regeneration of tissue. Hence, where the damage is towards the centre of the meniscus, the surgeon may need to perform meniscectomy for removal of the meniscus.